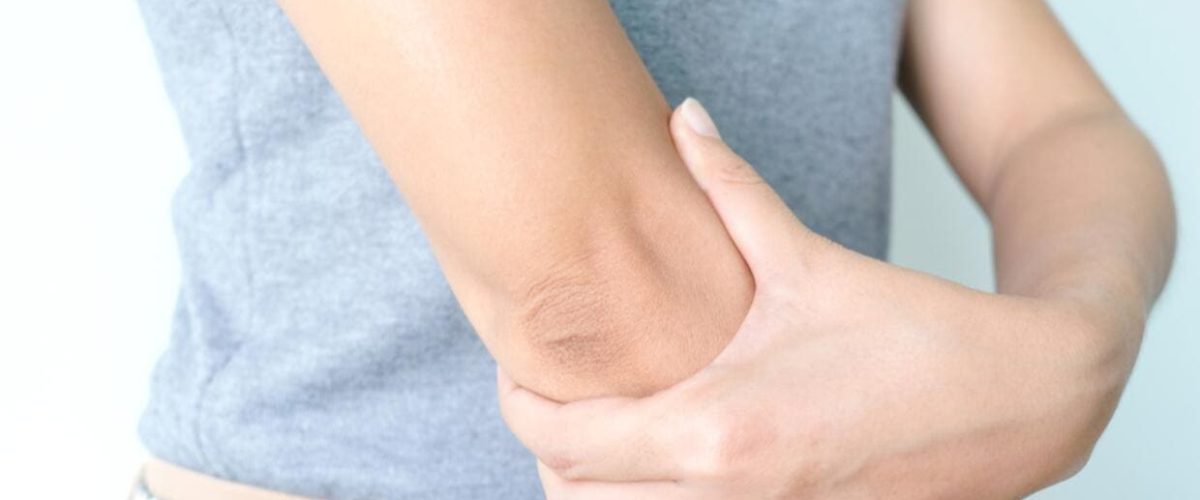
Bursitis is a painful condition that can limit daily activities and mobility. It occurs when the small fluid-filled sacs, known as bursae, become inflamed. Bursae are found near joints, acting as cushions between bones, muscles, and tendons. When they become irritated or swollen, the result is often pain and restricted movement, but you can get relief from bursitis.
If you’re experiencing joint pain, we are here to help. We provide quick access to knowledgeable providers for your concerns.
Here’s some more information from the Arthritis Foundation: https://www.arthritis.org/diseases/bursitis
What is Bursitis?
Bursitis is the inflammation of bursae, which are small sacs filled with fluid. These sacs reduce friction and help joints move smoothly. When bursae get irritated, they cause pain and swelling around joints.
Bursitis most commonly affects the shoulders, elbows, hips, and knees, though it can develop near any joint.
Common Types of Bursitis
There are various types of bursitis, each affecting different areas of the body. Here are some common types:
- Shoulder Bursitis (Subacromial Bursitis)
- This type involves inflammation in the shoulder joint, often linked to overhead activities.
- Elbow Bursitis (Olecranon Bursitis)
- Elbow bursitis results from pressure or injury to the elbow and is common in jobs with repetitive elbow movements or sports like tennis.
- Hip Bursitis (Trochanteric Bursitis)
- Hip bursitis often affects those who spend prolonged periods sitting, running, or standing.
- Knee Bursitis (Prepatellar Bursitis)
- This type commonly affects individuals who kneel frequently, like gardeners.
- Heel Bursitis (Retrocalcaneal Bursitis)
- This type develops at the back of the heel, often from tight shoes or excessive running.
Symptoms of Bursitis
Bursitis symptoms often develop gradually, worsening with movement or pressure on the affected area. Key symptoms include:
- Pain: Pain usually worsens with activity or direct pressure on the area.
- Swelling: Inflammation around the joint can cause visible swelling.
- Stiffness: Limited movement in the joint due to pain and inflammation.
- Tenderness: Affected areas may feel tender to the touch.
- Redness: Some cases involve visible redness, with or without infection.
Causes of Bursitis
Bursitis has various causes, often involving repetitive movements or injury. Common causes include:
- Repetitive Activities: Jobs or activities requiring repetitive joint use, like kneeling or lifting, can cause inflammation of bursae.
- Trauma: Direct injury or fall on a joint can irritate the bursa, causing inflammation.
- Infection: Infection can cause bursitis, either from direct wounds or systemic sources.
- Other Health Conditions: Conditions like gout, rheumatoid arthritis, and diabetes can lead to bursitis.
Diagnosing Bursitis
Diagnosis often begins with a history and physical exam to assess pain, swelling, and range of motion. Other tests may be needed:
- Imaging: X-rays, ultrasound, or MRI can visualize joint structures and identify any other issues.
- Aspiration: Removing fluid from the bursa can confirm infection or rule out other conditions.
- Blood Tests: Blood work may be conducted to detect an infection.
How to Get Relief from Bursitis
Bursitis treatment often focuses on relieving pain and reducing inflammation, and options vary depending on the cause and severity of bursitis.
1. Rest and Activity Modification
Rest is essential for healing, so reducing joint activity prevents further irritation and promotes healing.
2. Ice
Ice can help reduce swelling and numb pain. Apply ice for 15–20 minutes several times daily.
3. Medications
- Pain Relievers: Over-the-counter options like ibuprofen and naproxen can help reduce pain and inflammation.
- Topical Treatments: Creams and gels with anti-inflammatory ingredients may relieve local pain.
- Antibiotics: If bursitis is caused by infection, antibiotics are necessary to treat the underlying bacterial cause.
4. Physical Therapy
Physical therapy helps strengthen muscles around the affected joint, improving flexibility and reducing stress on the bursa. Exercises can prevent recurrent bursitis.
5. Steroid Injection
Corticosteroid injections can provide significant pain relief. These injections reduce inflammation quickly but are usually a short-term solution.
6. Aspiration
Aspiration involves removing excess fluid from the bursa using a needle. This can relieve pain and swelling.
7. Surgery
Surgery is a last resort, typically for cases that don’t improve despite treatment. The procedure removes the damaged bursa to relieve pain.
When to Seek Medical Help for Bursitis
If symptoms persist despite basic treatment, you should talk to your doctor. Seek help if you experience:
- Severe pain or swelling
- Difficulty moving the affected joint
- Symptoms of infection, such as redness or warmth
How Link Primary Care Helps With Bursitis Treatment
At Link Primary Care, we prioritize:
- Fast and Easy Access: Quick appointments to address concerns without long wait times.
- Personalized Relationships: We build trust and understanding with every patient.
- Affordable Care: Transparent pricing ensures peace of mind with no hidden costs.
With our approach, managing bursitis is straightforward and stress-free.
Schedule a one-on-one consultation with Dr. Jeffrey Davis using the following link:
https://calendly.com/jeffreydavis-linkprimarycare/link-primary-care-meeting
Get more information on our website at linkprimarycare.com